AK-47

The AK-47, or AK as it is officially known (Russian: Автомат Калашникова, Avtomat Kalashnikova, or ‘Kalashnikov’s Automatic Rifle’), also known as the Kalashnikov, is a selective-fire (semi-automatic and automatic), gas-operated 7.62×39 mm assault rifle, developed in the Soviet Union by Mikhail Kalashnikov. It is the originating firearm of the Kalashnikov rifle (or “AK”) family.
Design work on the AK-47 began in the last year of World War II (1945). In 1946, the AK-47 was presented for official military trials, and in 1948, the fixed-stock version was introduced into active service with selected units of the Soviet Army. An early development of the design was the AKS (S—Skladnoy or “folding”), which was equipped with an unfolding metal shoulder stock. In the spring of 1949, the AK-47 was officially accepted by the Soviet Armed Forces and used by the majority of the member states of the Warsaw Pact.
Saiga-12-Magnum

The Saiga-12 is a 12-gauge shotgun available in a wide range of configurations, patterned after the Kalashnikov series of rifles and named for the Saiga antelope. Like the Kalashnikov rifle variants, it is a rotating bolt, gas-operated gun that feeds from a box magazine. All Saiga-12 configurations are recognizable as Kalashnikov-pattern guns by the large lever-safety on the right side of the receiver, the optic mounting rail on the left side of the receiver and the large top-mounted dust cover held in place by the rear of the recoil spring assembly.
The Saiga-12 is manufactured by the arms division of Izhmash, in Russia. It was previously imported into the US by European American Armories, although their agreement expired in 2005 and Izhmash then began exporting through the Russian-American Armory Company. The current export import partner is Wolf Performance Arms. Izhmash also manufactures Saiga 20s and Saiga 410s in 20-gauge and .410 bore, as well as the Saiga semi-automatic hunting rifles in a number of centerfire calibers.
12-Gauge-Shotgun
The Mossberg® Maverick® 88 12 Gauge All-Purpose Pump-Action Shotgun features dual extractors, twin action bars, positive steel-to-steel lockup and an anti jam elevator for smooth, reliable performance that won’t let you down. The shotgun features a black synthetic stock and forearm for durability and a 6-round magazine capacity with 2-3/4″ shells and a 5-round capacity with 3″ shells. Bead sights help promote accurate aiming, and only 1 pin needs to be removed to field strip for easy maintenance.
SKS-Carbine

The SKS is a Soviet semi-automatic carbine chambered for the 7.62×39mm round, designed in 1943 by Sergei Gavrilovich Simonov. Its complete designation, SKS-45, is an initialism for “Samozaryadny Karabin sistemy Simonova”, 1945 (Russian: Самозарядный карабин системы Симонова, 1945; Self-loading Carbine of (the) Simonov system, 1945). The SKS-45 was manufactured at Tula Arsenal from 1949-1958 and at Izhevsk Arsenal in just 1953 and 1954, resulting in a total Soviet production of about 2.7 million carbines. In the early 1950s, the Soviets took the SKS carbine out of front-line service and replaced it with the AK-47; however, the SKS remained in second-line service for decades. It is still used as a ceremonial firearm today. The SKS was widely exported, and was also licensed for production by then Eastern Bloc nations, Romania and East Germany, as well as China, where it was designated the “Type 56 Carbine”. The East German version was known as the Karabiner S, the Albanian as the Model 561 and North Korean as the “Type 63”. The SKS is popular on the civilian surplus market as a hunting and marksmanship semi-automatic rifle in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and New Zealand. Its age and numbers make it relatively inexpensive to purchase, and steel cased 7.62x39mm ammunition is one of the least expensive centerfire cartridges currently on the market. The SKS was the second firearm to be chambered for the 7.62×39mm M43 round, with the first being the RPD.
Tanfoglio-Combat
The Tanfoglio Combat or Standard, also known as T(A)95 or EAA Witness Steel, is a modified clone of the Czech CZ-75/CZ-85 pistol. It is made in Gardone Val Trompia near Brescia, Italy by Fratelli Tanfoglio S.N.C.
The Tanfoglio Combat/Standard was introduced in 1997. The pistols are imported into the United States by European American Armory Inc. (EAA) and called the “Witness Steel”.
Russian-TT

The TT-33 was eventually replaced by the 8-round, 9×18mm Makarov PM pistol in 1952. Production of the TT-33 in Russia ended in 1954, but copies (licensed or otherwise) were also made by other countries. At one time or another most communist or Soviet bloc countries made a variation of the TT-33 pistol.
PM Makarov

The Makarov pistol or PM (Russian: Пистолет Макарова, Pistolet Makarova, literally Makarov’s Pistol) is a Russian semi-automatic pistol. Under the project leadership of Nikolay Fyodorovich Makarov, it became the Soviet Union’s standard military and police side arm in 1951.
Magnum 357
The .357 S&W Magnum (9×33mmR), or simply .357 Magnum, is a revolver cartridge with a .357-inch (9.07 mm) bullet diameter. It was created by Elmer Keith, Phillip B. Sharpe, and D. B. Wesson of firearms manufacturers Smith & Wesson and Winchester.
It is based upon Smith & Wesson’s earlier .38 Special cartridge. The .357 Magnum cartridge was introduced in 1934, and its use has since become widespread. This cartridge started the “Magnum era” of handgun ammunition.
Heckler-Koch-USP
The USP (Universelle Selbstladepistole or “universal self-loading pistol”) is a semi-automatic pistol developed in Germany by Heckler & Koch GmbH (H&K) of Oberndorf am Neckar as a replacement for the P7 series of handguns.
Glock
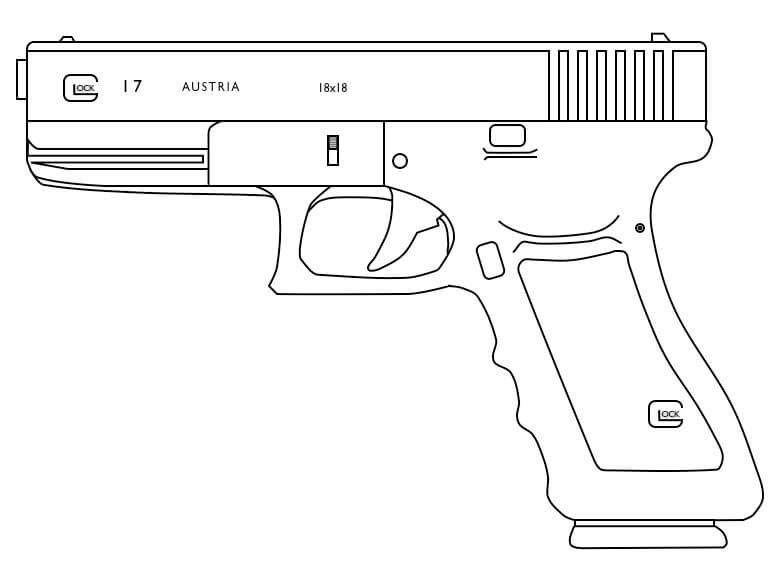
The Glock pistol sometimes referred to by the manufacturer as a Glock “Safe Action” pistol and colloquially as a Glock, is a series of polymer-framed, short recoil operated, locked breech semi-automatic pistols designed and produced by Glock Ges.m.b.H., located in Deutsch-Wagram, Austria. It entered Austrian military and police service by 1982 after it was the top performer on an exhaustive series of reliability and safety tests.
CZ-75

The CZ 75 is a pistol made by Česká zbrojovka Uherský Brod (CZUB) in the Czech Republic that has both semi-automatic and selective fire variants. First introduced in 1975, it is one of the original “wonder nines” featuring a staggered-column magazine, all-steel construction, and a hammer forged barrel. It is widely distributed throughout the world. It is the most common handgun in the Czech Republic.
SVD-Dragunov
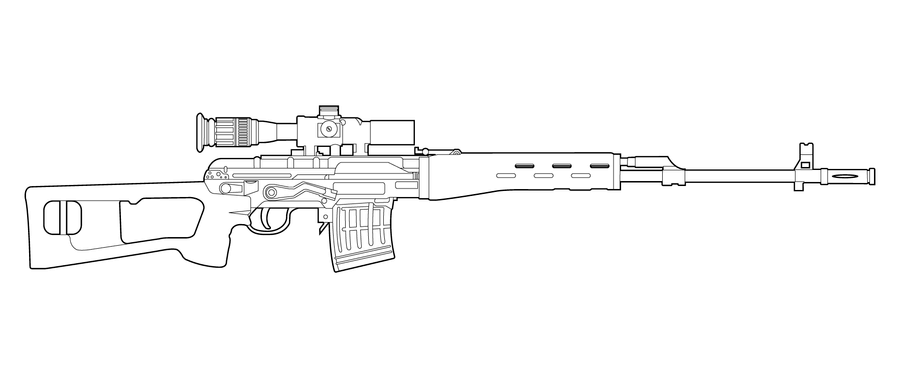
The Dragunov sniper rifle (formal Russian: Снайперская Винтовка системы Драгунова образца 1963 года Snayperskaya Vintovka sistem’y Dragunova obraz’tsa 1963 goda (SVD-63), officially “Sniper Rifle, System of Dragunov, Model of the Year 1963”) is a semi-automatic sniper/designated marksman rifle chambered in 7.62×54mmR and developed in the Soviet Union.
The Dragunov was designed as a squad support weapon since, according to Soviet and Soviet-derived military doctrines, the long-range engagement ability was lost to ordinary troops when submachine guns and assault rifles (which are optimized for close-range and medium-range, rapid-fire combat) were adopted. For that reason, it was originally named Самозарядная Винтовка системы Драгунова образца 1963 года “Self-Loading Rifle, System of Dragunov, Model of the Year 1963.”
Walther-G-22

The Walther G22 is a semi-automatic rifle chambered in the popular .22 Long Rifle cartridge, made by Walther. It is of bullpup design and constructed of polymer and steel.
Like most bullpup designs, it cannot be fired from the left hand due to the proximity of the ejection port and bolt handle to the shooter’s face. However, the stock is designed so that the ejection port and cocking handle can be relocated to the other side for left-handed shooters. A spare magazine, held by friction, is stored inside the polymer stock behind the magazine well. It was produced in matte black or green.
The G22 can achieve shot groups as small as 1.25 inches (32 mm) at 50 yards (46 meters). Spacers allow the butt of the stock to be adjusted to the user’s preference.